Methods in Spatial Research Fall 2021
Mapping Remotely - B
Satellite Grids & Google Static Maps API
This is a brief guide to using the Google Static Maps API (Application Programming Interface). In it we provide an example python script that allows you to download satellite/aerial imagery through the Google Static Maps API.
The (very simple) script in this tutorial was initially developed as part of the Center for Spatial Research’s work on In Plain Sight, an installation for the 16th International Architecture Exhibition of La Biennale di Venezia in 2018.
From this script it is possible to build images / projects like that of artist Josh Begley or like this:

This tutorial is not an introduction to APIs, nor is it an introduction to Python. However the tutorial walks you through how to batch download Google aerial or satellite imagery at a specified zoom level from a CSV of latitude and longitude coordinates. (See this post for a basic explanation of APIs and how they work, and this textbook is a great introduction to Python for data analysis.)
At a high level the process below is as follows:
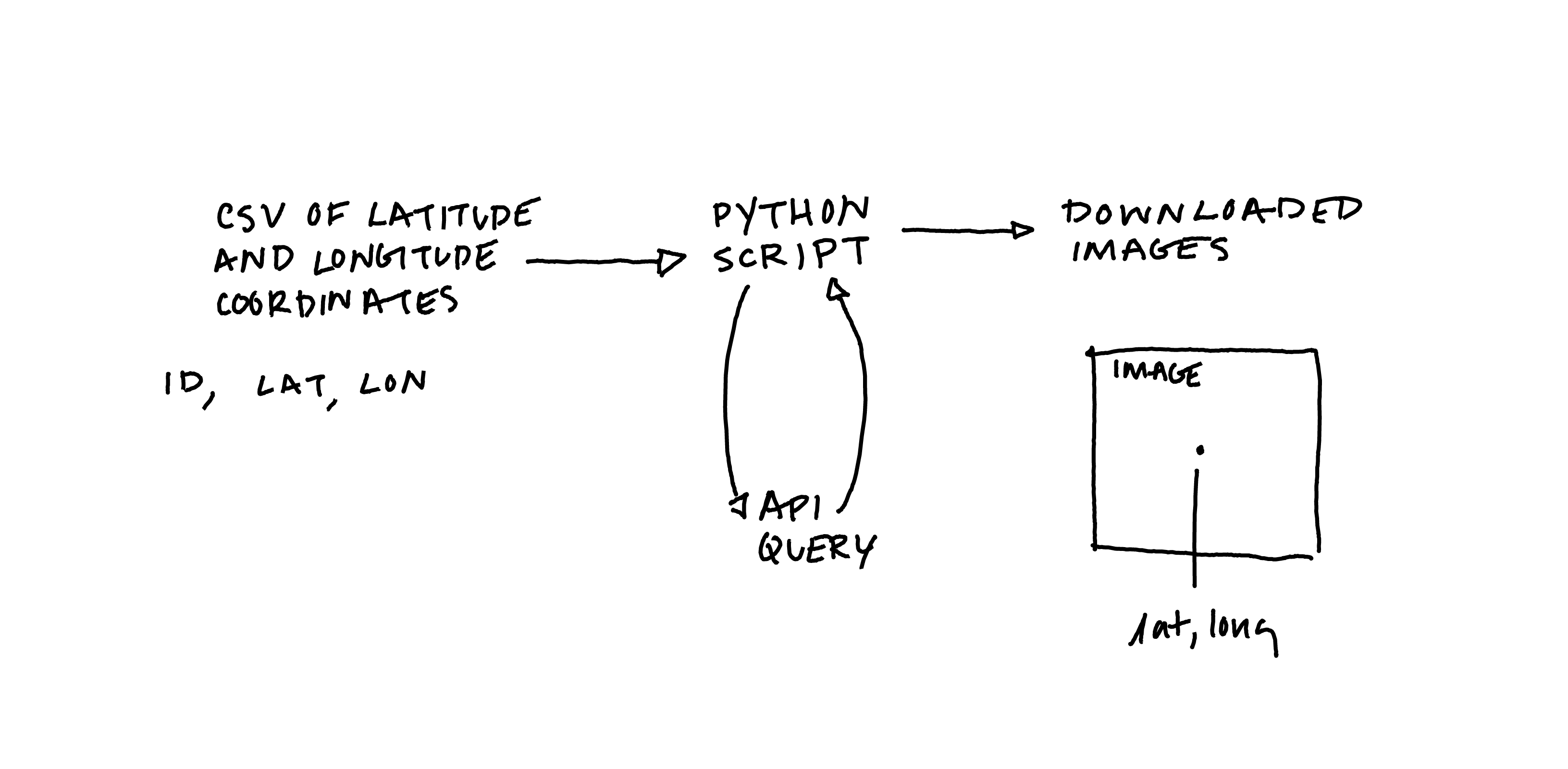
The outputs are image files (.png) that are not georeferenced and thus are best suited to use outside of a GIS software – combined into grids, assembled for an animation or GIF
Instructions
Prerequisites
Follow instructions for how to create a Google API key for the Static Maps API here. You must enable billing for your API key in order to run the script, you will not incur any charges for the scale of project outlined in this tutorial. Every Google SKU account is granted $200 per month in credits towards API usage, this translates to being able to download 100,000 images from Google’s Static Maps API for free each month. For more information on pricing see this page.
Method A: Google Colab
Follow these instructions if you are not already confident with running Python on your computer.
Launch Google Colab. This is a cloud-based programming environment that allows for the execution of Python code in the browser.
Step 1 - formatting a csv file with latitude and longitude coordinates
The script below expects a CSV file in a specific format, with three columns, no headers/column names, column 1 contains a unique id for each point, column 2 contains latitude coordinates, column 3 contains longitude coordinates. A sample of three points are shown below
101,39.203425,8.403248
102,27.884442,-97.259635
103,-16.432387,136.098233
Save the snippet above as test_points.csv, and/or change the latitude and longitude coordinates to locations of your choosing. You can do this by either pasting the text above into a text editor (making sure it is in plain text mode) and save it as test_points.csv. Or you can use some spreadsheet software (google sheets, or excel) and create a table with three columns containing the values above and save it as a .csv file. When you reuse this script on you own you will likely be using latitude and longitude coordinates gathered from elsewhere – you may export them from QGIS, or from EpiCollect, or manually input them into a spreadsheet. Before uploading them here be sure to format them exactly as shown above.
Step 2 - Setting up Colab and uploading the csv file
Open a new Google Colab notebook. This is the environment you will use to run the Python script which will query the Google Static Maps API.
First you will import necessary modules and use the colab data uploader to add your csv file to the notebook. To accomplish this run the following code in the first cell of your notebook (copy and paste the code then click the play button next to the cell to run):
from google.colab import files
import io
import pandas as pd
# upload data
uploaded = files.upload()
for fn in uploaded.keys():
print('User uploaded file "{name}" with length {length} bytes'.format(
name=fn, length=len(uploaded[fn])))
Use the Choose Files button that appears to navigate to the ‘test_points.csv’ file that you have just created.
Step 3 - Define and run Python function to query API
In the next cell of your notebook copy the following script, and run it. It defines a function to download satellite images based on input parameters:
nb copy this exactly and run it, do not chance anything !
# required modules
import requests
import csv
from io import open as iopen
# functions needed
def locationreader(uploaded_filename):
df = pd.read_csv(io.BytesIO(uploaded[uploaded_filename]), names=['id','lat','lng'])
list_df = df.values.tolist()
return(list_df)
# defining a function, it takes four parameters:
# the path to a csv file containing lat/lon coordinates
# your API key
# the zoom level you would your images to be downloaded as
# the size, in pixels of your images, the maximum is 640
# unless you have signed up for a premium account
def satellite_squares_colab(uploaded_filename,APIkey,zoom,size):
API_KEY = APIkey
base = "https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/staticmap?scale=2&size="
# this section reads the csv file
locations = locationreader(uploaded_filename)
# here we format a url to pass to the API for each row in the csv file
for location in locations:
ind, lat, lng = location
latlng = "center={},{}".format(lat, lng)
view = "zoom={}&maptype=satellite".format(zoom)
keys = "key={}".format(API_KEY)
url = "{}{}x{}&{}&{}&{}".format(base,size,size, latlng, view, keys)
# defining the name for the image files that will be downloaded
filename = "{}_{}.png".format(ind,zoom)
print(url)
print(filename)
res = requests.get(url)
if res.status_code == requests.codes.ok:
with iopen(filename, 'wb') as file:
file.write(res.content)
files.download(filename)
print(filename)
#here we tell the function to show us an error message if it is unable to download an image
else:
print(res.status_code)
print(url)
return False
Step 4 - Run the function to download your images
Once you have defined the function above call the function to download images. Replace the parameters in quotations with the name of the csv file you uploaded and your API key (both need to be enclosed in “ “)
satellite_squares_colab("uploaded_filename","yourAPIkey",13,640)
nb make sure you use the snippet above and not the code from step 3.
You should see the names of the images print in your notebook and images for the latitude and longitude coordinates specified in your csv file will begin to download to the downloads folder of your computer.
Method B - Python environment on your computer
If you already use Python (3) please follow these instructions.
The script requires three dependencies: requests csv and io, install these using your package manager if you do not already have them installed
Step 1: formatting a csv file with latitude and longitude coordinates
The script below expects a CSV file in a specific format, with three columns, no headers/column names, column 1 contains a unique id for each point, column 2 contains latitude coordinates, column 3 contains longitude coordinates. A sample of three points are shown below
101,39.203425,8.403248
102,27.884442,-97.259635
103,-16.432387,136.098233
Save the snippet above as test_points.csv, and/or change the latitude and longitude coordinates to locations of your choosing. You can do this by either pasting the text above into a text editor (making sure it is in plain text mode) and save it as test_points.csv. Or you can use some spreadsheet software (google sheets, or excel) and create a table with three columns containing the values above and save it as a .csv file. When you reuse this script on you own you will likely be using latitude and longitude coordinates gathered from elsewhere – you may export them from QGIS, or from EpiCollect, or manually input them into a spreadsheet. Before uploading them here be sure to format them exactly as shown above.
Step 2: defining the function to download images
Review the script below, it defines a function to download satellite images based on input parameters.
import requests
import csv
from io import open as iopen
# defining a function, it takes four parameters:
# the path to a csv file containing lat/lon coordinates
# your API key
# the zoom level you would your images to be downloaded as
# the size, in pixels of your images, the maximum is 640
def satellite_squares(csvforimport,APIkey,zoom,size):
API_KEY = APIkey
base = "https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/staticmap?scale=2&size="
locations = []
# this section reads the csv file
with open(csvforimport, 'rt') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
ind, lat, lng = str(row[0]),float(row[1]),float(row[2])
location = (ind, lat, lng)
locations.append(location)
# here we format a url to pass to the API for each row in the csv file
for location in locations:
ind, lat, lng = location
latlng = "center={},{}".format(lat, lng)
view = "zoom={}&maptype=satellite".format(zoom)
keys = "key={}".format(API_KEY)
url = "{}{}x{}&{}&{}&{}".format(base,size,size, latlng, view, keys)
# defining the name for the image files that will be downloaded
filename = "{}_{}.png".format(ind,zoom)
res = requests.get(url)
if res.status_code == requests.codes.ok:
with iopen(filename, 'wb') as file:
file.write(res.content)
print(filename)
#here we tell the function to show us an error message if it is unable to download an image
else:
print(res.status_code)
print(url)
return False
Run the script above in your preferred python environment, jupyter notebooks is a good option, you can also run it in a terminal
Once you have defined the function above call the function to download images.
satellite_squares("path-to-your-csv-file/test_points.csv","yourAPIkey",13,640)
Note on file paths: depending on where / how you are running this python script you may need to use either an absolute or a relative path to your csv files
Images for the latitude and longitude coordinates specified in your csv file will be downloaded into whatever location on your hard drive you are running the script from
Tutorial Deliverable
Upload to Canvas:
- the csv file you used and
- a screenshot of the directory on your computer where you have saved your downloaded images
Guide written by Dare Brawley based on tools used in producing In Plain Sight, an installation for the 16th International Architecture Exhibition of La Biennale di Venezia in 2018.